Continuous Variables
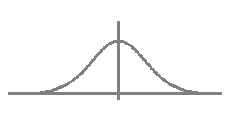
- A
random variable
is continuous
when
it can take on values on a continuous scale,
i.e., when
its range is uncountably infinite,
- Usually
continuous
random
variables arise from measuring.
- Examples include:
- GPA
of students.
- The
dimensional deviation of a product from its nominal diameter.
- Time
between calls arriving at a switchboard in an hour.
L.
K. Gaafar
