|
|
|
|
Introduction
|
|
According to the latest estimation conducted
by EDHR, Egypt’s population reached nearly
65335.6 hundreds in 2001. The highest population
density is in Cairo, where it reaches 2136.1
person per square kilometer against 63.7 person
per square kilometer in Egypt as a whole. In
Upper Egypt , it reached 97.8 persons compared
to 867.8 persons in Lower Egypt .In frontier
governorates it slightly exceeded 1 person per
K.m.2
(Egypt
Human Development Report 2003).
This indicates the heterogeneity of population
distribution across the inhabited areas in Egypt
which in turn affects the seriousness of the
population problem in Egypt.
|
|
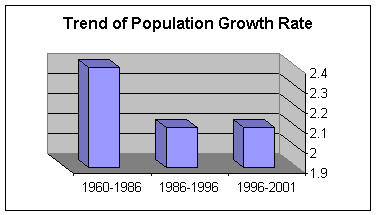
The Trend
in Population Growth
There has been continuous increase in the
size of the population, according to the results
of the last five censuses, in spite of the
decrease in fertility levels.
The population growth
rate reached 2.1% in 1996 -2001.
(Egypt
Human Development Report 2003). |
|
 |
|
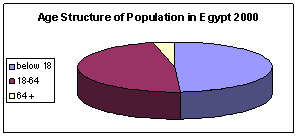
The Age Structure of Population
There has been a noticeable change in the
percentages of children below 18 years during
the last two decades. This category represented
47% of the total population in 1976, however it
decreased to 42% in 1996. Then it increased to
reach 49.2% in 2000. The proportion of the
elderly (65+) was 3.6% in 1976 and decreased to
3.2% in 1996. But it witnessed a slight increase
reaching 3.6% in 2000. (EDHS
2000)
Note: The DHS site
offers the facility of creating
statistical tables from the (EDHS 2000)
|
|
 |
|
|
|
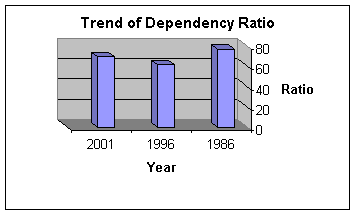
Dependency Ratio
It is widely known that Egypt
is characterized by a high proportion of
children, and the dependency ratio is considered
to be high according to international standards.
Dependency ratio was 77% in 1986, but it declined
substantially to 69.9% in 2001 according to Egypt Human Development Report 2003 (EHDR
2003). However this proportion is still high
compared to several developed and developing
countries.
Source:
Egypt Human Development Report 2003 (EHDR
2003).
|
|
|